Tìm hiểu về Saga pattern trong kiến trúc microservices
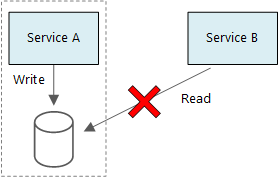
Trong kiến trúc microservices, mỗi service sẽ tự quản lý dữ liệu của mình và không chia sẻ trực tiếp với service khác. Điều này giúp giảm thiểu hoặc loại bỏ sự phụ thuộc giữa các service (loose coupling).
Khi một service thay đổi schema dữ liệu, ảnh hưởng của thay đổi này chỉ giới hạn trong service đó, không tác động đến các service khác. Ngoài ra, mỗi service có thể sử dụng hệ quản trị cơ sở dữ liệu riêng, tối ưu cho nhu cầu và đặc thù xử lý của chính nó.
Điều này đặt ra một thách thức: trong các hệ quản trị CSDL truyền thống, chúng ta có thể đảm bảo tính nhất quán dữ liệu nhờ cơ chế transaction. Tuy nhiên, khi dữ liệu được phân tán ở nhiều service với nhiều CSDL khác nhau, việc duy trì tính nhất quán trở nên phức tạp hơn.
Để giải quyết vấn đề này, có nhiều pattern được áp dụng, trong đó phổ biến nhất là Saga pattern. Saga định nghĩa một chuỗi các transaction cục bộ trong từng service. Nếu một bước trong chuỗi thất bại, Saga sẽ kích hoạt compensating transaction (transaction bù) để rollback những bước đã thực hiện trước đó, từ đó đảm bảo hệ thống vẫn duy trì được tính nhất quán dữ liệu.
Saga pattern
Saga pattern tách một logic transactions thành các local transaction trên từng services.
Mỗi một local transaction này sẽ làm:
Hoàn thành công việc trên một services
Cập nhật database của services đó.
Trigger event hoặc message để xử lý transaction tiếp theo
Nếu bất kì transaction nào bị lỗi, saga sẽ thực thi một loạt các transaction bù để phục hồi data đã bị thay đổi ở những local transaction đã chạy xong trước đó.
Cách triển khai Saga
Có hai cách cơ bản để triển khai Saga pattern: choreography (phân tán) và orchestration (tập trung)
Choreography
Trong phương pháp này, mỗi services sẽ trao đổi event mà không cần một người điểu khiển trung tâm. Mỗi services sẽ publish events để trigger local transaction tiếp theo ở các services khác. Các services sẽ lắng nghe ở những channel mà nó quan tâm, từ đó có thể hoàn thành các công việc mà services đó đảm nhận.
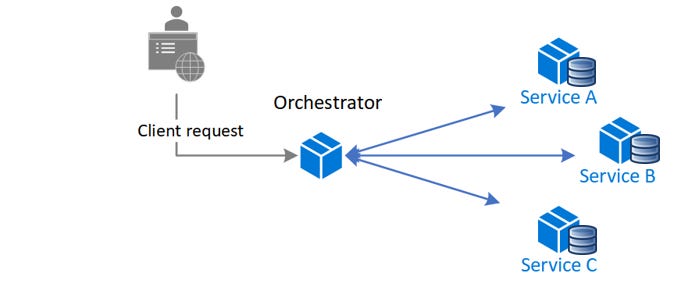
Orchestration
Như tên nó phương pháp này, cũng ta cần một người điều khiển trung tập (orchestrator), sẽ ra lệnh cho các services thực thi các transaction của services đó. Khi hoàn thành, services sẽ báo cáo kết quả cho orchestrator. Nếu một local transaction fail, orchestrator sẽ thực hiện handle các transaction bù ở những services đã hoàn thành trước đó để bảo đảm tính nhất quán của data.
Ví dụ cụ thể
Trong ví dụ này chúng ta sẽ xây dựng một e-commerce API đơn giản bằng FASTAPI, mĩnh sẽ triển khai cả 2 phương pháp choreography và orchestration để bạn đọc có thể dễ dàng hiểu hơn về 2 phương pháp này.
Hệ thống có 3 services chính:
order services: Tiếp nhận và tạo đơn hàng
payment service: Thanh toán
inventory service: quản lý hàng tồn kho
Nếu một service gặp lỗi:
Payment fail → hủy đơn hàng.
Inventory fail → hủy đơn hàng + refund payment.
Choreography
Kiến trúc:
Order Service nhận yêu cầu → tạo order (status:
PENDING) → gửiOrderCreated.Payment Service nhận event → trừ tiền → gửi
PaymentSucceededhoặcPaymentFailed.Inventory Service nhận
PaymentSucceeded→ giảm tồn kho → gửiInventoryReservedhoặcInventoryFailed.Nếu thất bại ở bất kỳ bước nào → phát event rollback để các service trước undo.
Order Service
# order_service.py
import asyncio, json
from fastapi import FastAPI
from aiokafka import AIOKafkaProducer, AIOKafkaConsumer
import uvicorn
BOOTSTRAP = "localhost:9092"
orders = {} # {order_id: {"status": str, "user_id": str, "amount": float}}
producer: AIOKafkaProducer = None
app = FastAPI()
@app.on_event("startup")
async def startup_event():
global producer
producer = AIOKafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers=BOOTSTRAP)
await producer.start()
# Consumers for multiple topics
consumer = AIOKafkaConsumer(
"payment_failed", "inventory_reserved", "inventory_failed",
bootstrap_servers=BOOTSTRAP,
group_id="order-service"
)
await consumer.start()
async def listen_events():
async for msg in consumer:
data = json.loads(msg.value.decode())
order_id = data["order_id"]
if msg.topic == "payment_failed":
orders[order_id]["status"] = "CANCELLED"
print(f"⚠️ Order {order_id} cancelled due to payment failure")
elif msg.topic == "inventory_reserved":
orders[order_id]["status"] = "DONE"
print(f"✅ Order {order_id} completed successfully")
elif msg.topic == "inventory_failed":
orders[order_id]["status"] = "CANCELLED"
print(f"⚠️ Order {order_id} cancelled due to inventory failure")
asyncio.create_task(listen_events())
@app.on_event("shutdown")
async def shutdown_event():
await producer.stop()
@app.post("/orders")
async def create_order(order_id: str, user_id: str, amount: float):
orders[order_id] = {"status": "PENDING", "user_id": user_id, "amount": amount}
event = {"order_id": order_id, "user_id": user_id, "amount": amount}
await producer.send_and_wait("order_created", json.dumps(event).encode())
print(f"📤 Order created: {event}")
return {"status": "Order created", "order_id": order_id}
@app.get("/orders/{order_id}")
async def get_order(order_id: str):
return {"order_id": order_id, **orders.get(order_id, {"status": "NOT_FOUND"})}
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
Chúng ta có một FastAPI nhận order từ user. Order service sẽ tạo một order với thông tin về item_id, user_id và trạng thái là "PENDING". Sau đó sẽ send message vô topic order_created với thông tin về order mới được tạo. Cùng lúc đó nó cũng lắng nghe từ inventory services, nếu inventory thành công, order service sẽ update order tưng ứng thành DONE, nếu có lỗi trong quá trình xảy ra thì sẽ update order thành CANCELLED
Payment Service
import asyncio, json, random
from aiokafka import AIOKafkaConsumer, AIOKafkaProducer
BOOTSTRAP = "localhost:9092"
async def main():
consumer = AIOKafkaConsumer("order_created", bootstrap_servers=BOOTSTRAP, group_id="payment-service")
producer = AIOKafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers=BOOTSTRAP)
await consumer.start(); await producer.start()
print("💰 Payment Service started")
try:
async for msg in consumer:
order = json.loads(msg.value.decode())
print(f"Processing payment for order {order['order_id']}")
# Giả lập thanh toán
if random.choice([True, False]):
topic = "payment_succeeded"
print(f"✅ Payment OK for order {order['order_id']}")
else:
topic = "payment_failed"
print(f"❌ Payment FAIL for order {order['order_id']}")
await producer.send_and_wait(topic, json.dumps(order).encode())
finally:
await consumer.stop(); await producer.stop()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
Payment services lắng nghe từ order services và tiến hành thanh toán khi có message tới. Ở đây chúng ta giả lập viêc thành toán thành công hoặc thất bại bằng một hàm random. Nếu thành công, payment service sẽ gửi một message vào topic payment_succeeded ngược lại sẽ gửi vào topic payment_failed đính kèm order detail.
Inventory Service
import asyncio, json, random
from aiokafka import AIOKafkaConsumer, AIOKafkaProducer
BOOTSTRAP = "localhost:9092"
async def main():
consumer = AIOKafkaConsumer("payment_succeeded", bootstrap_servers=BOOTSTRAP, group_id="inventory-service")
producer = AIOKafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers=BOOTSTRAP)
await consumer.start(); await producer.start()
print("📦 Inventory Service started")
try:
async for msg in consumer:
order = json.loads(msg.value.decode())
print(f"Checking inventory for order {order['order_id']}")
if random.choice([True, False]):
topic = "inventory_reserved"
print(f"✅ Inventory reserved for order {order['order_id']}")
else:
topic = "inventory_failed"
print(f"❌ Inventory not available for order {order['order_id']}")
await producer.send_and_wait(topic, json.dumps(order).encode())
finally:
await consumer.stop(); await producer.stop()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
Ở Inventory Service cũng tương tự như payment services. Nó nhận message từ topic payment_succeeded, sau đó tiến thành kiểm tra, nếu thành công sẽ gửi order vô topic inventory_reserved ngược lại sẽ là topic inventory_failed
Orchestration
Quy trình với Saga Orchestration sẽ như sau:
User tạo order → Order Service lưu
PROCESSING→ phátorder_created.Orchestrator nhận
order_created→ gọi Payment Service.Payment Service trả
OKhoặcFAIL.Orchestrator nhận kết quả:
FAIL→ hủy đơn.OK→ gọi Inventory Service.
Inventory Service trả
OKhoặcFAIL.Orchestrator nhận kết quả:
OK→ hoàn tất đơn.FAIL→ hủy đơn.
Đầu tiền order service sẽ nhận request từ user để tạo một order
from fastapi import FastAPI
from aiokafka import AIOKafkaProducer, AIOKafkaConsumer
import asyncio, json, uvicorn
BOOTSTRAP = "localhost:9092"
orders = {}
producer: AIOKafkaProducer = None
app = FastAPI()
@app.on_event("startup")
async def start():
global producer
producer = AIOKafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers=BOOTSTRAP)
await producer.start()
consumer = AIOKafkaConsumer(
"mark_done", "mark_cancelled",
bootstrap_servers=BOOTSTRAP,
group_id="order-service"
)
await consumer.start()
async def listen():
async for msg in consumer:
data = json.loads(msg.value.decode())
oid = data["order_id"]
if msg.topic == "mark_done":
orders[oid]["status"] = "DONE"
elif msg.topic == "mark_cancelled":
orders[oid]["status"] = "CANCELLED"
print("Orders:", orders)
asyncio.create_task(listen())
@app.post("/create_order/{oid}")
async def create_order(oid: str):
orders[oid] = {"id": oid, "status": "PROCESSING"}
await producer.send_and_wait("order_created", json.dumps({"order_id": oid}).encode())
return {"msg": "Order created", "order_id": oid}
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run(app, port=8001)
Ở đây chúng ta cần một orchestrator service để điều phối mọi việc
from aiokafka import AIOKafkaConsumer, AIOKafkaProducer
import asyncio, json
BOOTSTRAP = "localhost:9092"
async def main():
producer = AIOKafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers=BOOTSTRAP)
await producer.start()
consumer = AIOKafkaConsumer(
"order_created", "payment_result", "inventory_result",
bootstrap_servers=BOOTSTRAP,
group_id="orchestrator"
)
await consumer.start()
async for msg in consumer:
data = json.loads(msg.value.decode())
oid = data["order_id"]
if msg.topic == "order_created":
await producer.send_and_wait("payment", json.dumps(data).encode())
elif msg.topic == "payment_result":
if data["status"] == "OK":
await producer.send_and_wait("check_inventory", json.dumps(data).encode())
else:
await producer.send_and_wait("mark_cancelled", json.dumps(data).encode())
elif msg.topic == "inventory_result":
if data["status"] == "OK":
await producer.send_and_wait("mark_done", json.dumps(data).encode())
else:
await producer.send_and_wait("mark_cancelled", json.dumps(data).encode())
asyncio.run(main())
tương tự cho payment
from aiokafka import AIOKafkaConsumer, AIOKafkaProducer
import asyncio, json, random
BOOTSTRAP = "localhost:9092"
async def main():
producer = AIOKafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers=BOOTSTRAP)
await producer.start()
consumer = AIOKafkaConsumer(
"payment",
bootstrap_servers=BOOTSTRAP,
group_id="payment-service"
)
await consumer.start()
async for msg in consumer:
data = json.loads(msg.value.decode())
# Random giả lập thanh toán OK hoặc FAIL
status = random.choice(["OK", "FAIL"])
await producer.send_and_wait("payment_result", json.dumps({"order_id": data["order_id"], "status": status}).encode())
asyncio.run(main())
Và Inventory:
from aiokafka import AIOKafkaConsumer, AIOKafkaProducer
import asyncio, json, random
BOOTSTRAP = "localhost:9092"
async def main():
producer = AIOKafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers=BOOTSTRAP)
await producer.start()
consumer = AIOKafkaConsumer(
"check_inventory",
bootstrap_servers=BOOTSTRAP,
group_id="inventory-service"
)
await consumer.start()
async for msg in consumer:
data = json.loads(msg.value.decode())
# Random giả lập tồn kho OK hoặc FAIL
status = random.choice(["OK", "FAIL"])
await producer.send_and_wait("inventory_result", json.dumps({"order_id": data["order_id"], "status": status}).encode())
asyncio.run(main())
Kết luận
Hy vọng tới đây bạn đã hiểu cách Saga Pattern hoạt động trong kiến trúc microservice.
Pattern này đặc biệt hữu ích khi:
Bạn cần đảm bảo tính nhất quán dữ liệu trong môi trường distributed system mà vẫn loại bỏ sự phụ thuộc chặt chẽ giữa các service.
Cần thực hiện rollback hoặc các hành động bù trừ khi một transaction thất bại.
Nếu bạn thấy bài viết hữu ích, hãy subscribe để nhận thêm những bài viết chuyên sâu về kiến trúc hệ thống và microservices.
Đừng ngần ngại để lại câu hỏi hoặc chia sẻ trải nghiệm của bạn với Saga Pattern ở phần bình luận nhé!
Đọc thêm:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/microservices/design/data-considerations
https://www.f5.com/company/blog/nginx/event-driven-data-management-microservices
https://www.baeldung.com/cs/saga-pattern-microservices




nếu mà dùng cách tập trung, vậy giao tiếp giữa các service với nhau thì admin dùng http hay grpc, cách nào sẽ tốt hơn không hay cách nào cũng được
vậy mình thấy 2 cách phân tán hay tập trung cũng giống nhau phải không admin , có 1 service hoặc broker để handle các status của các service phải không bạn, vậy thì chia ra 2 cách triển khai để làm gì