Xây dựng một ứng dụng Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) - P2
Tiếp nối phần 1, chúng ta sẽ nâng cấp chatbot bằng cách bổ sung khả năng lưu trữ lịch sử hội thoại và phản hồi theo ngữ cảnh, giúp mô phỏng cách trò chuyện tự nhiên của con người.
Trong phần này, chúng ta sẽ cải tiến chatbot ở phần 1, cho phép chatbot ghi nhớ lịch sử hội thoại, tương tác khi giao tiếp và thực hiện retrieval nhiều bước.
Có 2 phương pháp để xây nhưng chatbot như trên:
Chains: Cho mỗi user input, tối đa một câu query được thực thi trong bước retrieval
Agents: Cho phép sử dụng LLM để thực thì nhiều câu query trong retrieval step
Chain
Ở phần 1, chúng ta đã xây dựng một chatbot dựa trên input của người dùng, truy xuất các tài liệu liên quan và tạo câu trả lời dựa trên thông tin từ những tài liệu đó. Để mô phỏng cách trò chuyện tự nhiên giống con người hơn, chúng ta sẽ lưu trữ toàn bộ quá trình này dưới dạng một chuỗi các message. Cụ thể:
Input từ người dùng sẽ được lưu dưới dạng
HumanMessage;Truy vấn đến vector store sẽ là một
AIMessagecó kèm theo tool calls;Các tài liệu được truy xuất sẽ được ghi lại dưới dạng
ToolMessage;Câu trả lời cuối cùng sẽ là một
AIMessage
Tools
Trong LangChain, abstraction "tool" liên kết một hàm Python với một schema mô tả tên hàm, chức năng và các tham số đầu vào mà nó mong đợi.
Các tool này có thể được truyền vào các chat model, hỗ trợ tính năng tool calls, cho phép mô hình yêu cầu thực thi một hàm cụ thể với các đầu vào cụ thể.
Định nghĩa một tools trong ví dụ của chúng ta:
from langchain_core.tools import tool
@tool(response_format="content_and_artifact")
def retrieve(query: str):
"""Retrieve information related to a query."""
retrieved_docs = vector_store.similarity_search(query, k=2)
serialized = "\n\n".join(
(f"Source: {doc.metadata}\nContent: {doc.page_content}")
for doc in retrieved_docs
)
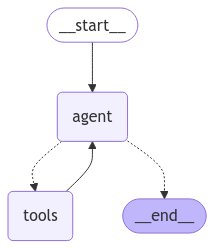
return serialized, retrieved_docsChúng ta xây dựng 1 graph với 3 node:
Một node nhận user input: hoặc tạo câu query hoặc trả về câu trả lời ngay.
Một node gọi tool để retrieve từ vector_store
Một node generate câu trả lòi từ output từ tool calling function.
from langchain_core.messages import SystemMessage
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode
# Step 1: Generate an AIMessage that may include a tool-call to be sent.
def query_or_respond(state: MessagesState):
"""Generate tool call for retrieval or respond."""
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools([retrieve])
response = llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])
# MessagesState appends messages to state instead of overwriting
return {"messages": [response]}
# Step 2: Execute the retrieval.
tools = ToolNode([retrieve])
# Step 3: Generate a response using the retrieved content.
def generate(state: MessagesState):
"""Generate answer."""
# Get generated ToolMessages
recent_tool_messages = []
for message in reversed(state["messages"]):
if message.type == "tool":
recent_tool_messages.append(message)
else:
break
tool_messages = recent_tool_messages[::-1]
# Format into prompt
docs_content = "\n\n".join(doc.content for doc in tool_messages)
system_message_content = (
"You are an assistant for question-answering tasks. "
"Use the following pieces of retrieved context to answer "
"the question. If you don't know the answer, say that you "
"don't know. Use three sentences maximum and keep the "
"answer concise."
"\n\n"
f"{docs_content}"
)
conversation_messages = [
message
for message in state["messages"]
if message.type in ("human", "system")
or (message.type == "ai" and not message.tool_calls)
]
prompt = [SystemMessage(system_message_content)] + conversation_messages
# Run
response = llm.invoke(prompt)
return {"messages": [response]}Tiếp theo, chúng ta sẽ kết hợp tất cả các thành phần lại thành một đối tượng graph. Lưu ý rằng tại điểm bắt đầu "query_or_respond", chúng ta sử dụng add_conditional_edges để xác định luồng đi: nếu không có tool được gọi thì kết thúc tại đây, còn nếu có, luồng sẽ tiếp tục đến node xử lý tool.
from langgraph.graph import END
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode, tools_condition
graph_builder.add_node(query_or_respond)
graph_builder.add_node(tools)
graph_builder.add_node(generate)
graph_builder.set_entry_point("query_or_respond")
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges(
"query_or_respond",
tools_condition,
{END: END, "tools": "tools"},
)
graph_builder.add_edge("tools", "generate")
graph_builder.add_edge("generate", END)
graph = graph_builder.compile()
from IPython.display import Image, display
display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))Testing:
input_message = "Hello"
for step in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": input_message}]},
stream_mode="values",
):
step["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
## Output:
================================ [1m Human Message [0m=================================
Hello
================================== [1m Ai Message [0m==================================
Hello! How can I assist you today?Chúng ta có thể thấy không có tool calling nào được gọi, tiếp tục với ví dụ khác có yêu cầu tool calling và generate câu trả lời từ tool calling result.
input_message = "What is Task Decomposition?"
for step in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": input_message}]},
stream_mode="values",
):
step["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
## Output
================================ [1m Human Message [0m=================================
What is Task Decomposition?
================================== [1m Ai Message [0m==================================
Tool Calls:
retrieve (call_dLjB3rkMoxZZxwUGXi33UBeh)
Call ID: call_dLjB3rkMoxZZxwUGXi33UBeh
Args:
query: Task Decomposition
================================= [1m Tool Message [0m=================================
Name: retrieve
Source: {'source': 'https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/'}
Content: Fig. 1. Overview of a LLM-powered autonomous agent system.
Component One: Planning#
A complicated task usually involves many steps. An agent needs to know what they are and plan ahead.
Task Decomposition#
Chain of thought (CoT; Wei et al. 2022) has become a standard prompting technique for enhancing model performance on complex tasks. The model is instructed to “think step by step” to utilize more test-time computation to decompose hard tasks into smaller and simpler steps. CoT transforms big tasks into multiple manageable tasks and shed lights into an interpretation of the model’s thinking process.
Source: {'source': 'https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/'}
Content: Tree of Thoughts (Yao et al. 2023) extends CoT by exploring multiple reasoning possibilities at each step. It first decomposes the problem into multiple thought steps and generates multiple thoughts per step, creating a tree structure. The search process can be BFS (breadth-first search) or DFS (depth-first search) with each state evaluated by a classifier (via a prompt) or majority vote.
Task decomposition can be done (1) by LLM with simple prompting like "Steps for XYZ.\n1.", "What are the subgoals for achieving XYZ?", (2) by using task-specific instructions; e.g. "Write a story outline." for writing a novel, or (3) with human inputs.
================================== [1m Ai Message [0m==================================
Task Decomposition is the process of breaking down a complicated task into smaller, manageable steps. It often involves techniques like Chain of Thought (CoT), which encourages models to think step by step, enhancing performance on complex tasks. This approach allows for a clearer understanding of the task and aids in structuring the problem-solving process.Quản lý trạng thái của lịch sử hội thoại
Trong giao tiếp hàng ngày, con người thường ghi nhớ nội dung cuộc trò chuyện và phản hồi dựa trên những gì đã được nói trước đó. Tương tự, các mô hình chat cũng cần khả năng ghi nhớ lịch sử hội thoại. LangGraph hỗ trợ lưu trữ lịch sử này vào cơ sở dữ liệu, từ đó có thể truy xuất và cung cấp lại cho mô hình để duy trì mạch hội thoại.
LangGraph có hỗ trợ lưu vào những database khác nhau như SQLite or Postgres, trong ví dụ này chúng ta có thể sử dụng in-memory đơn giản để xem cách thức LangGraph hoạt động
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver
memory = MemorySaver()
graph = graph_builder.compile(checkpointer=memory)
# Specify an ID for the thread
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "abc123"}}Test thử:
input_message = "What is Task Decomposition?"
for step in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": input_message}]},
stream_mode="values",
config=config,
):
step["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
## Output:
================================ [1m Human Message]===
What is Task Decomposition?
================================== [1m Ai Message]===
Tool Calls:
retrieve (call_JZb6GLD812bW2mQsJ5EJQDnN)
Call ID: call_JZb6GLD812bW2mQsJ5EJQDnN
Args:
query: Task Decomposition
================================= [1m Tool Message]===
Name: retrieve
Source: {'source': 'https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/'}
Content: Fig. 1. Overview of a LLM-powered autonomous agent system.
Component One: Planning#
A complicated task usually involves many steps. An agent needs to know what they are and plan ahead.
Task Decomposition#
Chain of thought (CoT; Wei et al. 2022) has become a standard prompting technique for enhancing model performance on complex tasks. The model is instructed to “think step by step” to utilize more test-time computation to decompose hard tasks into smaller and simpler steps. CoT transforms big tasks into multiple manageable tasks and shed lights into an interpretation of the model’s thinking process.
Source: {'source': 'https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/'}
Content: Tree of Thoughts (Yao et al. 2023) extends CoT by exploring multiple reasoning possibilities at each step. It first decomposes the problem into multiple thought steps and generates multiple thoughts per step, creating a tree structure. The search process can be BFS (breadth-first search) or DFS (depth-first search) with each state evaluated by a classifier (via a prompt) or majority vote.
Task decomposition can be done (1) by LLM with simple prompting like "Steps for XYZ.\n1.", "What are the subgoals for achieving XYZ?", (2) by using task-specific instructions; e.g. "Write a story outline." for writing a novel, or (3) with human inputs.
================================== [1m Ai Message]==
Task Decomposition is a technique used to break down complicated tasks into smaller, manageable steps. It involves using methods like Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting, which encourages the model to think step by step, enhancing performance on complex tasks. This process helps to clarify the model's reasoning and makes it easier to tackle difficult problems.Tiếp tục hỏi 1 câu hỏi khác liên quan tời câu hỏi trước đó
input_message = "Can you look up some common ways of doing it?"
for step in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": input_message}]},
stream_mode="values",
config=config,
):
step["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
Output:
================================ [1m Human Message
Can you look up some common ways of doing it?
================================== [1m Ai Message
Tool Calls:
retrieve (call_kjRI4Y5cJOiB73yvd7dmb6ux)
Call ID: call_kjRI4Y5cJOiB73yvd7dmb6ux
Args:
query: common methods of task decomposition
================================= [1m Tool Message
Name: retrieve
Source: {'source': 'https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/'}
Content: Tree of Thoughts (Yao et al. 2023) extends CoT by exploring multiple reasoning possibilities at each step. It first decomposes the problem into multiple thought steps and generates multiple thoughts per step, creating a tree structure. The search process can be BFS (breadth-first search) or DFS (depth-first search) with each state evaluated by a classifier (via a prompt) or majority vote.
Task decomposition can be done (1) by LLM with simple prompting like "Steps for XYZ.\n1.", "What are the subgoals for achieving XYZ?", (2) by using task-specific instructions; e.g. "Write a story outline." for writing a novel, or (3) with human inputs.
Source: {'source': 'https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/'}
Content: Fig. 1. Overview of a LLM-powered autonomous agent system.
Component One: Planning#
A complicated task usually involves many steps. An agent needs to know what they are and plan ahead.
Task Decomposition#
Chain of thought (CoT; Wei et al. 2022) has become a standard prompting technique for enhancing model performance on complex tasks. The model is instructed to “think step by step” to utilize more test-time computation to decompose hard tasks into smaller and simpler steps. CoT transforms big tasks into multiple manageable tasks and shed lights into an interpretation of the model’s thinking process.
================================== [1m Ai Message
Common ways of performing Task Decomposition include: (1) using Large Language Models (LLMs) with simple prompts like "Steps for XYZ" or "What are the subgoals for achieving XYZ?", (2) employing task-specific instructions such as "Write a story outline" for specific tasks, and (3) incorporating human inputs to guide the decomposition process.Chúng ta có thể thấy câu trả lời ở câu hỏi thứ 2 có được sử dụng ngữ cách ở câu hỏi đầu.
Agents
Ở phương pháp thứ hai, chúng ta sẽ sử dụng agents để xây dựng graph. Bản thân mô hình ngôn ngữ (LLM) không thể tự thực hiện hành động — nó chỉ có khả năng sinh văn bản đầu ra. Agents khai thác sức mạnh của LLM để quyết định hành động nào cần thực hiện và cách thực hiện chúng. Trong trường hợp này, chúng ta sẽ dùng LangGraph để xây dựng các agent.
Vì agents có khả năng ra quyết định trong thời gian chạy (run-time), nên chúng đặc biệt phù hợp với các tình huống phức tạp, nơi luồng xử lý không thể đoán trước như khi sử dụng Chain thông thường.
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
agent_executor = create_react_agent(llm, [retrieve], checkpointer=memory)
display(Image(agent_executor.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))Output:
Điểm khác biệt chính so với cách triển khai trước đây là thay vì kết thúc bằng bước sinh câu trả lời cuối cùng, quá trình gọi tool trong mô hình này sẽ quay lại bước gọi LLM ban đầu. Khi đó, mô hình có thể lựa chọn giữa việc trả lời dựa trên ngữ cảnh đã truy xuất, hoặc tiếp tục tạo thêm một lệnh gọi tool khác để lấy thêm thông tin.
Test
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "def234"}}
input_message = (
"What is the standard method for Task Decomposition?\n\n"
"Once you get the answer, look up common extensions of that method."
)
for event in agent_executor.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": input_message}]},
stream_mode="values",
config=config,
):
event["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
## Output:
================================ [Human Message
What is the standard method for Task Decomposition?
Once you get the answer, look up common extensions of that method.
================================== [1m Ai Message
Tool Calls:
retrieve (call_Y3YaIzL71B83Cjqa8d2G0O8N)
Call ID: call_Y3YaIzL71B83Cjqa8d2G0O8N
Args:
query: standard method for Task Decomposition
================================= [1m Tool Message
Name: retrieve
Source: {'source': 'https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/'}
Content: Tree of Thoughts (Yao et al. 2023) .....
Source: {'source': 'https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/'}
Content: Fig. 1. Overview of a LLM-powered autonomous agent system.
Component One: .....
================================== [1m Ai Message
Tool Calls:
retrieve (call_2JntP1x4XQMWwgVpYurE12ff)
Call ID: call_2JntP1x4XQMWwgVpYurE12ff
Args:
query: common extensions of Task Decomposition methods
================================= [1m Tool Message
Name: retrieve
Source: {'source': 'https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/'}
Content: Tree of Thoughts (Yao et al. 2023) ....
Source: {'source': 'https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/'}
Content: Fig. 1. Overview of a LLM-powered autonomous agent system.
Component One: Planning# ......
================================== [1m Ai Message
The standard method for task decomposition involves using techniques such as Chain of Thought (CoT), where a model is instructed to "think step by step" to break down complex tasks into smaller, more manageable components. This approach enhances model performance by allowing for more thorough reasoning and planning. Task decomposition can be accomplished through various means, including:
1. Simple prompting (e.g., asking for steps to achieve a goal).
2. Task-specific instructions (e.g., asking for a story outline).
3. Human inputs to guide the decomposition process.
### Common Extensions of Task Decomposition Methods:
1. **Tree of Thoughts**: This extension builds on CoT by not only decomposing the problem into thought steps but also generating multiple thoughts at each step, creating a tree structure. The search process can employ breadth-first search (BFS) or depth-first search (DFS), with each state evaluated by a classifier or through majority voting.
These extensions aim to enhance reasoning capabilities and improve the effectiveness of task decomposition in various contexts.Với agents:
Tạo câu query cho việc tìm kiếm
Task DecompositionNhận được phản hồi từ tool, sau đó tạo câu query thứ hai về “
common extensions of Task Decomposition methods”Khi đã có đầy đủ thông tin, tạo câu trả lời
Kết luận
Trong bài post này, chúng ta đã đi qua 2 khái niệm:
Chains: Phù hợp để xây dựng các ứng dụng có luồng xử lý dữ liệu cố định và chỉ cần thực hiện một truy vấn duy nhất cho mỗi lần người dùng nhập liệu.
Agents: Thích hợp cho các ứng dụng yêu cầu tương tác linh hoạt, cho phép mô hình thực hiện nhiều truy vấn liên tiếp trong một phiên làm việc.
Nếu bạn có thắc mắc gì, đừng ngần ngại đặt câu hỏi bên dưới.
Đọc thêm
https://python.langchain.com/docs/concepts/tools/
https://python.langchain.com/docs/tutorials/qa_chat_history